

테셀레이션은 간격이나 겹침 없이 반복되는 패턴으로 도형을 배열하는 것을 말합니다.

이때, 합동 정다각형 모양만 사용하는 경우에 정규 테셀레이션이라 부릅니다.
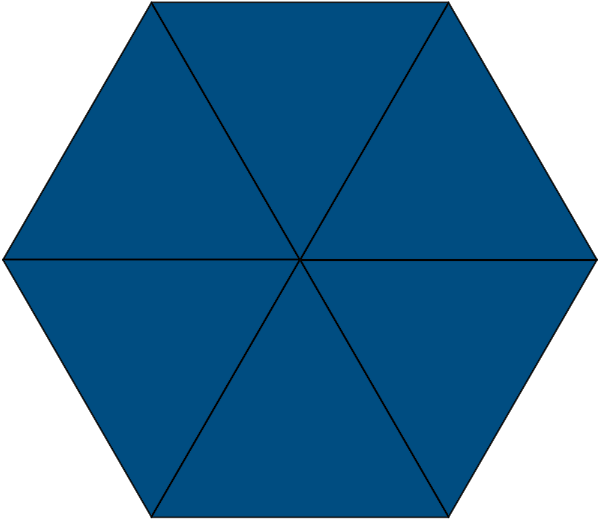


같은 넓이를 갖는 정다각형 중 둘레의 길이의 합이 가장 작게하려면 정육각형으로 테셀레이션 해야하는데
만약 3차원에서 비슷한걸 하려면 어떤 모양이어야 할까요?
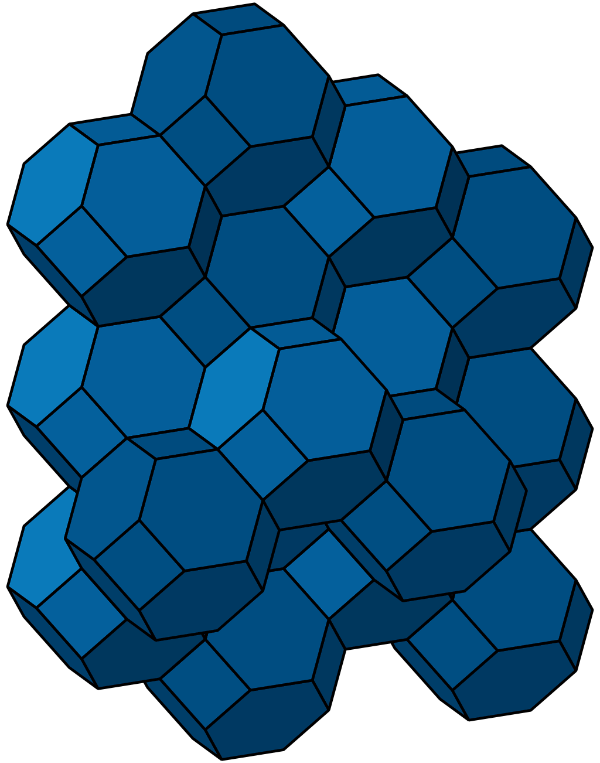
3차원도 벌집모양과 비슷하게 육각형과 사각형을 이용한 도형 만들면 될 것 같지만
1887년 켈빈(절대온도의 그 Kelvin)이 제안한 “깍은 정육면체 벌집(bitruncated cubic honeycomb)”

오각형과 육각형을 짜맞춘 도형이 더 효율적인 것이 밝혀졌습니다.
100년 뒤인 1997년 발표된 “웨이어-펠란 구조(Weaire–Phelan structure)”
아직 이보다 더 효율적인 구조가 있는지 밝혀지지 않았는데, 과연 어떤 모양이 최선일까요?
테셀레이션(Tessellation)은 도형을 겹치지 않게 배열하여 평면이나 공간을 완전히 채우는 패턴을 말합니다. 이러한 패턴은 수학, 예술, 건축 등 여러 분야에서 사용됩니다.
2차원 테셀레이션: 2차원 테셀레이션은 주로 정다각형을 사용하여 평면을 완전히 채우는 패턴을 생성합니다. 일반적으로 다음과 같은 세 가지 유형으로 분류할 수 있습니다.
- 정규 테셀레이션: 정다각형 하나만 사용하여 평면을 완전히 채우는 테셀레이션입니다. 정삼각형, 정사각형, 정육각형의 3가지 경우가 존재합니다.
- 준정규 테셀레이션: 두 개 이상의 정다각형을 사용하여 평면을 완전히 채우는 테셀레이션입니다. 8가지 경우가 존재합니다.
- 불규칙 테셀레이션: 불규칙한 다각형을 사용하여 평면을 완전히 채우는 테셀레이션입니다. 많은 다양한 경우가 존재합니다.
3차원 테셀레이션: 3차원 테셀레이션은 공간을 완전히 채우기 위해 입체 도형을 사용합니다. 플라토닉 입체(정다면체)와 아치메데스 입체를 포함한 다양한 종류가 있습니다.
- 플라토닉 입체: 정육면체, 정사면체, 정팔면체, 정이십면체, 정십이면체의 5가지 경우가 존재합니다.
- 아치메데스 입체: 13가지 경우가 존재하며, 각 모서리에서 동일한 다면체가 만나는 특징을 가집니다.
- 깍은 벌집 모양 (Truncated octahedron): 켈빈이 제안한 깍은 벌집 모양은 정육면체와 정팔면체를 결합한 입체도형입니다. 이 도형은 8개의 정육각형과 6개의 정사각형 면으로 구성되어 있으며, 모서리를 깍아낸 것처럼 보입니다.이러한 패턴은 공간효율성과 구조적 안정성이 뛰어납니다. 그 결과, 이 도형은 많은 과학적 연구와 공학적 응용에서 찾아볼 수 있습니다.
- 웨이어-펠란 구조 (Weaire-Phelan structure): 웨이어-펠란 구조는 3차원 공간을 채우는 효율적인 방법 중 하나로, 두 종류의 볼록 다면체인 펠란 P와 펠란 Q로 구성되어 있습니다. 이 구조는 켈빈이 제안한 깍은 벌집 모양보다 적은 표면적을 가집니다. 웨이어-펠란 구조는 표면 에너지를 최소화하는 데 효과적이기 때문에, 거품이나 세포 구조와 같은 자연 현상에서 관찰됩니다.
소개
타일링으로도 알려진 테셀레이션은 타일이라고 불리는 반복되는 모양을 사용하여 간격이나 겹침 없이 2차원 표면을 덮는 것을 가리키는 중요한 수학적 개념이다. 그것은 기하학, 예술, 컴퓨터 그래픽 등을 포함한 다양한 분야에서 수많은 응용 프로그램을 가지고 있다. 테셀레이션에 대한 포괄적인 이해의 필요성이 점점 커지고 있으며, 전문가들이 그 주제에 대한 철저한 이해를 갖는 것이 중요하다.
정의
테셀레이션은 모든 방향으로 반복되는 평면의 타일링 패턴으로 정의된다. 즉, 그것은 틈이나 겹침 없이 평평한 표면을 덮는 반복되는 모양의 패턴이다. 테셀레이션에 사용되는 모양을 타일이라고 한다. 테셀레이션에 사용할 수 있는 세 가지 유형의 타일이 있습니다: 일반, 반정규, 불규칙.
테셀레이션의 종류
정기적인 테셀레이션
일반 테셀레이션은 동일한 각도로 가장자리와 가장자리를 만나는 일치하는 일반 다각형 타일로 구성된 타일링 패턴이다. 일반 테셀레이션의 가장 흔한 예는 정사각형 타일로 구성된 정사각형 타일링이다.
반정규 테셀레이션
반정규 테셀레이션은 동일한 각도로 가장자리에서 가장자리를 만나는 두 가지 이상의 일반 다각형 타일로 구성된 타일링 패턴이다. 반정규 테셀레이션의 예는 등변 삼각형과 정사각형으로 구성된 육각형 타일링이다.
불규칙한 테셀레이션
불규칙한 테셀레이션은 일반 다각형 타일이 아닌 모양으로 구성된 타일링 패턴이다. 모양은 어떤 기하학적 모양일 수 있으며, 같은 각도로 가장자리에서 가장자리를 만날 필요가 없다. 불규칙한 테셀레이션의 예는 무작위 모양으로 구성된 타일 패턴이다.
3D 테셀레이션
3차원의 테셀레이션으로도 알려진 3D 테셀레이션은 반복되는 모양으로 3차원 공간을 타일링하는 것을 포함하는 수학적 개념이다. 2차원 테셀레이션과 마찬가지로, 3D 테셀레이션에 사용된 모양은 틈이나 겹침 없이 함께 맞아야 한다.
3D 테셀레이션에서 사용되는 모양은 일반적으로 평평한 면과 직선 모서리를 가진 3차원 모양인 다면체이다. 3D 테셀레이션에 사용되는 다면체의 몇 가지 일반적인 예로는 큐브, 사면체 및 팔면체가 있다.
3D 테셀레이션은 건축, 엔지니어링 및 컴퓨터 그래픽을 포함한 많은 중요한 응용 분야를 가지고 있다. 건축에서, 3D 테셀레이션은 건물 표면과 인테리어에 반복되는 패턴과 모양을 만드는 데 사용될 수 있다. 엔지니어링에서, 3D 테셀레이션은 특정 강도와 안정성 특성을 가진 반복되는 구조를 만드는 데 사용될 수 있다. 컴퓨터 그래픽에서, 3D 테셀레이션은 더 효율적이고 시각적으로 매력적인 방식으로 물체와 질감을 표현하는 데 사용될 수 있다.
전반적으로, 3D 테셀레이션은 수많은 응용 프로그램을 가지고 있으며 다양한 분야에서 새로운 발견과 혁신으로 이어질 수 있기 때문에 전문가들이 이해할 수 있는 매혹적이고 중요한 개념이다.
정리
테셀레이션과 관련된 몇 가지 정리가 있으며, 그 중 일부는 다음과 같다:
피타고라스 정리
피타고라스 정리는 직각 삼각형에서, 하변의 길이의 제곱(오른 각도의 반대쪽)은 다른 두 면의 길이의 제곱의 합과 같다고 말한다.
$c^2 = a^2 + b^2$
이 정리는 테셀레이션 패턴에서 측면의 길이를 결정하는 데 유용하다.
앵글-앵글 정리
각도-각 정리는 한 삼각형의 두 각도가 다른 삼각형의 두 각도와 같다면, 삼각형은 비슷하다고 말한다.
이 정리는 두 개의 테셀레이션 패턴의 유사성을 결정하는 데 유용하다.
성질
테셀레이션과 관련된 몇 가지 속성이 있으며, 그 중 일부는 다음과 같습니다:
일치
일치는 크기와 모양이 동일한 두 모양의 특성을 말한다. 테셀레이션에서, 패턴이 모든 방향으로 반복되기 위해서는 타일이 일치해야 한다.
대칭
대칭은 모양을 두 개의 일치하는 부분으로 나누는 대칭 축을 가진 모양의 특성을 말한다. 테셀레이션에서, 패턴이 모든 방향으로 반복되기 위해서는 타일이 대칭이 있어야 한다.
번역 대칭
번역 대칭은 번역 또는 위치의 변화에서 불변하는 모양의 속성을 말한다. 테셀레이션에서, 패턴이 모든 방향으로 반복되기 위해서는 타일이 번역 대칭을 가져야 한다.
응용 프로그램
다양한 분야에서 테셀레이션의 몇 가지 응용이 있으며, 그 중 일부는 다음과 같다:
예술과 디자인
테셀레이션은 그래픽 디자인, 퀼트, 직물 등을 포함한 예술과 디자인에 널리 사용된다. 예술가와 디자이너는 종종 테셀레이션 패턴을 사용하여 만족스러운 미학으로 반복적인 디자인을 만든다.
기하학
테셀레이션은 기하학에서 중요한 개념이며 기하학적 모양, 패턴 및 변형 연구에 사용된다. 그것은 또한 대칭과 정규 다각형의 특성에 대한 연구에 사용된다.
컴퓨터 그래픽
테셀레이션은 2차원 물체와 질감을 나타내기 위해 컴퓨터 그래픽에 사용된다. 예를 들어, 테셀레이션은 구의 표면과 같은 표면을 나타내기 위해 컴퓨터 그래픽에서 사용된다.
건축
테셀레이션은 벽과 바닥에 장식 패턴을 만들기 위해 건축에 사용된다. 예를 들어, 모자이크와 타일 패턴은 종종 장식 효과를 만들기 위해 건축에서 사용된다.
결론
결론적으로, 테셀레이션은 예술과 디자인, 기하학, 컴퓨터 그래픽 및 건축을 포함한 다양한 분야에서 수많은 응용 분야를 가진 강력한 수학적 개념이다. 그 중요성과 잠재적인 용도를 완전히 이해하기 위해 전문가들이 이해해야 할 중요한 개념이다.
"Unlocking the Mosaic Mystery: Exploring the Infinite Possibilities of Tessellation"
Introduction
Tessellation, also known as tiling, is an important mathematical concept that refers to the covering of a two-dimensional surface without any gaps or overlaps using repeating shapes called tiles. It has numerous applications in various fields, including geometry, art, computer graphics, and more. The need for a comprehensive understanding of tessellation is increasingly growing, making it important for experts to have a thorough understanding of the subject.
Definition
A tessellation is defined as a tiling pattern of the plane that repeats in all directions. In other words, it is a repeated pattern of shapes that covers a flat surface without any gaps or overlaps. The shapes used in a tessellation are called tiles. There are three types of tiles that can be used in a tessellation: regular, semi-regular, and irregular.
Types of Tessellation
Regular Tessellation
A regular tessellation is a tiling pattern made up of congruent regular polyggon tiles that meet edge to edge with equal angles. The most common example of a regular tessellation is the square tiling, which is made up of square tiles.
Semi-Regular Tessellation
A semi-regular tessellation is a tiling pattern made up of two or more types of regular polygon tiles that meet edge to edge with equal angles. An example of a semi-regular tessellation is the hexagonal tiling, which is made up of equilateral triangles and squares.
Irregular Tessellation
An irregular tessellation is a tiling pattern made up of shapes that are not regular polyggon tiles. The shapes can be any geometric shape, and they do not have to meet edge to edge with equal angles. An example of an irregular tessellation is a tiling pattern made up of random shapes.
Theorems
There are several theorems related to tessellation, some of which are:
The Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides.
$c^2 = a^2 + b^2$
This theorem is useful in determining the lengths of sides in a tessellation pattern.
The Angle-Angle Theorem
The Angle-Angle Theorem states that if two angles of one triangle are equal to two angles of another triangle, then the triangles are similar.
This theorem is useful in determining the similarity of two tessellation patterns.
Properties
There are several properties related to tessellation, some of which are:
Congruence
Congruence refers to the property of two shapes being identical in size and shape. In a tessellation, the tiles must be congruent in order for the pattern to repeat in all directions.
Symmetry
Symmetry refers to the property of a shape having an axis of symmetry, which divides the shape into two congruent parts. In a tessellation, the tiles must have symmetry in order for the pattern to repeat in all directions.
Translational Symmetry
Translational symmetry refers to the property of a shape being invariant under a translation, or a change in position. In a tessellation, the tiles must have translational symmetry in order for the pattern to repeat in all directions.
Applications
There are several applications of tessellation in various fields, some of which are:
Art and Design
Tessellation is widely used in art and design, including graphic design, quilting, textiles, and more. Artists and designers often use tessellation patterns to create repetitive designs with a pleasing aesthetic.
Geometry
Tessellation is an important concept in geometry and is used in the study of geometric shapes, patterns, and transformations. It is also used in the study of symmetry and the properties of regular polygggons.
Computer Graphics
Tessellation is used in computer graphics to represent two-dimensional objects and textures. For example, tessellation is used in computer graphics to represent surfaces, such as the surface of a sphere.
Architecture
Tessellation is used in architecture to create decorative patterns on walls and floors. For example, mosaics and tile patterns are often used in architecture to create a decorative effect.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tessellation is a powerful mathematical concept that has numerous applications in various fields, including art and design, geometry, computer graphics, and architecture. It is an important concept for experts to understand in order to fully appreciate its significance and potential uses.
Keywords
tessellation, tiling, mathematics, art, design, geometry, computer graphics, architecture, regular, semi-regular, irregular, Pythagorean Theorem, Angle-Angle Theorem, congruence, symmetry, translational symmetry.
3D Tessellations
3D tessellation, also known as tessellation in three dimensions, is a mathematical concept that involves tiling three-dimensional spaces with repeating shapes. Just as in two-dimensional tessellations, the shapes used in 3D tessellations must fit together without any gaps or overlaps.
In 3D tessellation, the shapes used are typically polyhedra, which are three-dimensional shapes with flat faces and straight edges. Some common examples of polyhedra used in 3D tessellation include cubes, tetrahedra, and octahedra.
3D tessellation has a number of important applications, including in architecture, engineering, and computer graphics. In architecture, 3D tessellation can be used to create repeating patterns and shapes on building surfaces and interiors. In engineering, 3D tessellation can be used to create repeating structures with specific strength and stability properties. In computer graphics, 3D tessellation can be used to represent objects and textures in a more efficient and visually appealing way.
Overall, 3D tessellation is a fascinating and important concept for experts to understand, as it has numerous applications and can lead to new discoveries and innovations in a variety of fields.

You know what's cooler than magic? Math.
포스팅이 좋았다면 "좋아요❤️" 또는 "구독👍🏻" 해주세요!



